Project Sunroof, a “twenty percent time” project of Google’s Carl Elkin could bring ground-breaking surge in the use of Solar Panels in houses. Carl was surprised at the number of people who were reluctant to utilize solar energy, being a member of Solarize Massachusetts movement. The general reaction was “my roof is not sunny enough” or “it’s too expensive”. Carl was determined to find a solution, which was simple to use for laymen but as accurate as it can get. The conventional method of calculating solar panel requirements for your roof involves an actual expert visiting the site with a fish-eye camera and clicking pics from the four corners, to analyze the light availability.
How is Google Tool Calculating Roof Area
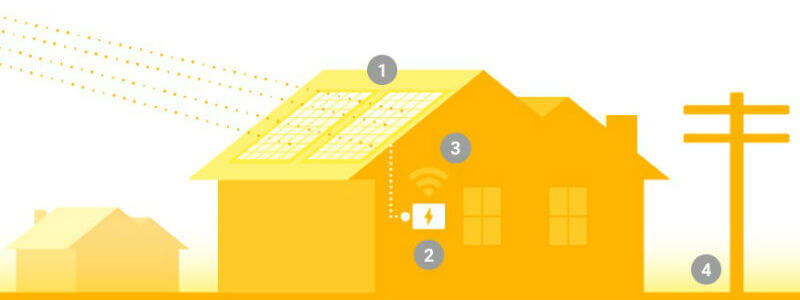
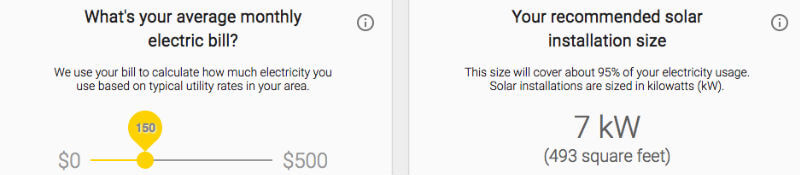
The project utilizes Google’s complex resources already available. High resolution aerial mapping, the same as in Google Earth, is used to create 3D model of your roof. Using artificial intelligence, solar exposure is compounded based on the size of roof, obstructions to sunlight like trees or building, possible sun position with respect to your area and the resulting exposure and the weather pattern in the area over the years. Based on this data and your input of current monthly electric bill, Sunroof calculates your savings over 20-year lease. All you need to do is, head over to the site and enter your address! The pivotal technology being used here is the 3D model of world that does shadow casting, which helps to predict whether there will be light or shade, on each day of the year, round the clock. For this, Google doesn’t use satellite imagery, but high quality imagery available from Google’s airplanes which shoot imagery, as former’s resolution is not good enough.
According to samples provided, a small roof which has 5 hours of sunlight a day on average, can produce savings of $13,000 across a period of 20-year lease. Project Sunroof goes one step further to connect you to the local solar panel vendors to assist you in the panel installation. The project started as a pilot project, with coverage in San Francisco Bay Area, Fresno and Boston in August, 2015. Right now it has expanded to 42 states, covering 43 million buildings, roughly. With the kind of resources at its disposal, one shouldn’t be surprised if Google expands the project to other countries. The Project was one of the winners of 2016 UN Momentum for change award. This award is given to replicable projects contributing towards addressing global climate change. Google has added a Data Explorer feature to the original project, which aggregates data in a locality or city or state. This tool should help government bodies to determine solar potential of a particular area, to implement necessary measures towards adapting solar energy.
Δ